1. Spring Security 인증 구조 이해
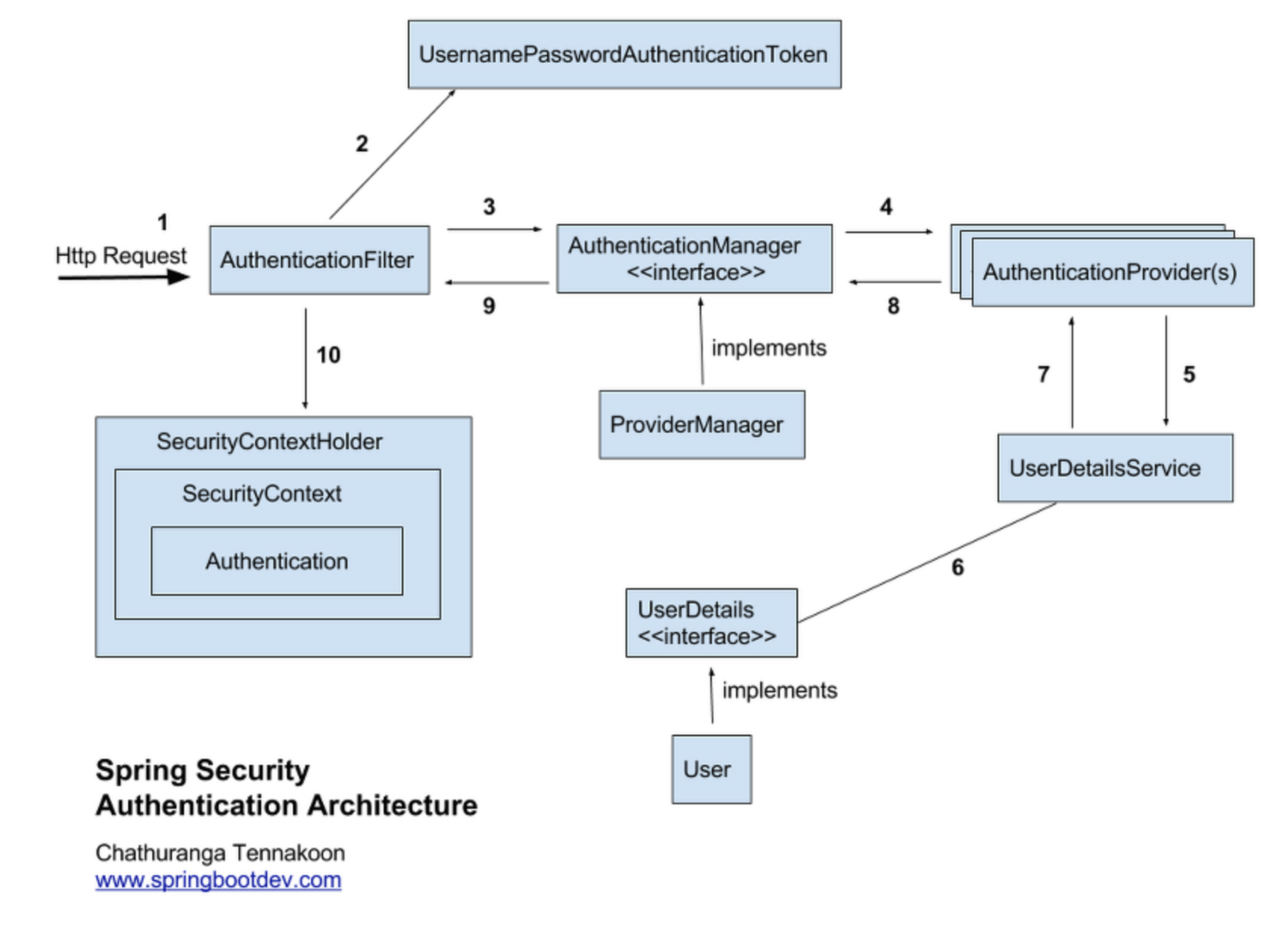
1. HTTP Request (인증 요청)
2. AuthenticationFilter를 거친다. (UsernamePasswordAuthenticationFilter)
- HttpServletRequest를 인터셉트하여 AuthenticationManager에 Authentication 객체를 만들어 UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken)에 전달한다.
3. AuthenticationManager는 AuthenticationFilter로부터 인증 객체를 전달받는다.
- 인증 객체 (UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken)
4. 해당 인증 객체를 통해 인증을 진행하는 AuthenticationProvider를 찾아 인증 객체(UsernamePasswordAuthenticationToken)를 전달하고 인증을 요청한다.
5. 6. 7. Provier에서 Service를 호출하여 UserDetails를 통해 인증을 진행한다. (DB 데이터 조회 및 검증)
8. 9. 10. 인증 성공 시 사용자 데이터가 담긴 Authentication 객체를 SecurityContextHolder에 저장하고 AuthenticationSuccessHandle를 실행한다.
(실패 시 AuthenticationFailureHandler 실행)
JWT 토큰을 사용하기 위해 새로운 AuthenticationFilter, AuthenticationProvier, AuthenticationToken, UserService를 재정의 해주었습니다.
2. 로그인 과정
(1) UserController (HTTP Request)
@Slf4j
@RestController
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class UserController {
private final UserService userService;
private final AuthenticationManager authenticationManager;
@PostMapping("/api/users/login")
public ResponseEntity<LoginResponseDto> login(@RequestBody LoginRequestDto request) {
JwtAuthenticationToken jwtAuthenticationToken = new JwtAuthenticationToken(
request.getEmail(), request.getPassword());
Authentication authentication = authenticationManager.authenticate(jwtAuthenticationToken);
JwtAuthenticationToken authenticated = (JwtAuthenticationToken) authentication;
JwtAuthentication principal = (JwtAuthentication) authenticated.getPrincipal();
User user = (User) authenticated.getDetails();
Boolean isFirstLogin = Boolean.FALSE;
if (user.getLastLoginAt() == null) {
isFirstLogin = Boolean.TRUE;
}
userService.updateLastLoginAt(user);
LoginResponseDto responseDto = LoginResponseDto.fromEntity(principal.accessToken,
principal.refreshToken, user, isFirstLogin);
return ResponseEntity.ok().body(responseDto);
}
}
- 클라이언트에서 로그인 요청 시 해당 이메일과, 비밀번호를 전달한다.
- 해당 이메일과, 비밀번호를 이용해서 JwtAuthenticationToken 객체를 생성한다.
- 생성한 JwtAuthenticationToken 객체를 AuthenticationManager에게 전달한다.
(2) JwtAuthenticationToken (인증 객체)
@ToString
public class JwtAuthenticationToken extends AbstractAuthenticationToken {
private final Object principal;
private String credentials;
public JwtAuthenticationToken(String principal, String credentials) {
super(null);
super.setAuthenticated(false);
this.principal = principal;
this.credentials = credentials;
}
public JwtAuthenticationToken(Object principal, String credentials, Collection<? extends GrantedAuthority> authorities) {
super(authorities);
super.setAuthenticated(true);
this.principal = principal;
this.credentials = credentials;
}
@Override
public String getCredentials() {
return credentials;
}
@Override
public Object getPrincipal() {
return principal;
}
@Override
public void setAuthenticated(boolean authenticated) {
if (authenticated) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Cannot set this token to trusted.");
}
super.setAuthenticated(false);
}
@Override
public void eraseCredentials() {
super.eraseCredentials();
credentials = null;
}
}
- JwtAuthenticationToken은 인증 객체로 사용된다.
- principal, credentials 두 가지의 필드를 가진다.
- Authentication 전
- principal : 이메일
- credentials : 비밀번호
- Authenticaion 후 (DB 데이터 조회 및 검증)
- principal : JwtAuthentication 객체 (새롭게 custom 하여 구현)
- credentials : 인증 후에는 비밀번호가 필요 없기 때문에 null 값을 넣을 것이다. (JwtAuthenticationProvier 로직)
- Authentication 전
(3) JwtAuthentication
@ToString
public class JwtAuthentication {
public final String accessToken;
public final String refreshToken;
public final String email;
public JwtAuthentication(String accessToken, String refreshToken, String email) {
if(accessToken.isEmpty()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("token must be provided");
}
if(email.isEmpty()) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("email must be provided");
}
this.accessToken = accessToken;
this.refreshToken = refreshToken;
this.email = email;
}
}
- 인증 후 (DB 데이터 조회 및 검증) JwtAuthenticationToken의 principal 필드에 들어오는 객체
- accessToken, refreshToken, email 필드를 가진다.
- 인증에 성공한다면 서버는 해당 사용자에게 accessToken과 refreshToken을 생성해서 값을 반환해준다. (AuthenticationProvier 로직)
(4) JwtAuthenticationProvider
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class JwtAuthenticationProvider implements AuthenticationProvider {
private final Jwt jwt;
private final UserService userService;
private final RefreshTokenService refreshTokenService;
@Override
public Authentication authenticate(Authentication authentication) throws AuthenticationException {
JwtAuthenticationToken jwtAuthenticationToken = (JwtAuthenticationToken) authentication;
return processUserAuthentication(
String.valueOf(jwtAuthenticationToken.getPrincipal()),
jwtAuthenticationToken.getCredentials()
);
}
@Override
public boolean supports(Class<?> authentication) {
return (JwtAuthenticationToken.class.isAssignableFrom(authentication));
}
private Authentication processUserAuthentication(String principal, String credentials) {
try {
User user = userService.login(principal, credentials);
List<GrantedAuthority> authorities = user.getAuthorities();
String accessToken = getAccessToken(user.getEmail(), authorities);
String refreshToken = getRefreshToken(user.getEmail(), authorities);
JwtAuthenticationToken authenticationToken = new JwtAuthenticationToken(
new JwtAuthentication(accessToken, refreshToken, user.getEmail()), null, authorities);
authenticationToken.setDetails(user);
return authenticationToken;
} catch (IllegalArgumentException e) {
throw new BadCredentialsException(e.getMessage());
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new AuthenticationServiceException(e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
private String getAccessToken(String email, List<GrantedAuthority> authorities) {
String[] roles = authorities.stream().map(GrantedAuthority::getAuthority)
.toArray(String[]::new);
return jwt.createAccessToken(Jwt.Claims.from(email, roles));
}
private String getRefreshToken(String email, List<GrantedAuthority> authorities) {
String[] roles = authorities.stream().map(GrantedAuthority::getAuthority)
.toArray(String[]::new);
return refreshTokenService.issueRefreshToken(Jwt.Claims.from(email, roles));
}
}
- 다시 Controller에서 생성한 JwtAuthenticationToken 객체를 AuthenticationManager에게 전달되었다.
- AuthenticationManager는 AuthenticationProvider를 찾아 JwtAuthenticationToken 객체를 전달하고 인증을 요청한다.
- AuthenticationProvider는 userService를 사용하여 해당 이메일과 비밀번호를 사용하여 DB 조회 검증이 일어난다.
- 인증에 통과하면 AccessToken, RefreshToken을 생성하고 JwtAuthentication객체 상태로 JwtAuthenticationToken principal 필드 안에 넣는다.
- JWT Token의 생성은 Jwt class를 구현하여 책임과 역할을 분리하였다.
(5) UserService
public class UserService {
private final UserRepository userRepository;
private final InterestService interestService;
private final PasswordEncoder passwordEncoder;
private final EmailService emailService;
public User login(String email, String credentials) {
User user = userRepository.findByEmail(email)
.orElseThrow(LoginFailureException::new);
user.checkPassword(passwordEncoder, credentials);
return user;
}
}
- UserService는 AuthenticationProvider에서 전달받은 이메일과 비밀번호를 DB에 저장된 값과 비교한다.
(6) Return 값
인증이 완료되면 클라이언트에게 생성된 AccessToken, RefreshToken을 전달한다.
{
"accessToken": "{AccessToken}",
"refreshToken": "{RefreshToken}"
}
3. AccessToken을 통한 인증 과정
이제 클라이언트에서 Header에 AccessToken과 함께 API 요청된다.
JwtAuthenticationFilter
@Slf4j
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class JwtAuthenticationFilter extends OncePerRequestFilter {
private final String accessHeaderKey;
private final String refreshHeaderKey;
private final Jwt jwt;
@Override
protected void doFilterInternal(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
FilterChain chain) throws ServletException, IOException {
if (SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication() == null) {
Optional<String> maybeAccessToken = getAccessToken(request);
Optional<String> maybeRefreshToken = getRefreshToken(request);
if (maybeAccessToken.isPresent() && maybeRefreshToken.isEmpty()) {
String accessToken = maybeAccessToken.get();
Jwt.Claims claims = verify(accessToken);
log.debug("Jwt parse result: {}", claims);
String email = claims.getEmail();
List<GrantedAuthority> authorities = getAuthorities(claims);
if (isNotEmpty(email) && authorities.size() > 0) {
JwtAuthenticationToken authentication = new JwtAuthenticationToken(
new JwtAuthentication(accessToken, null, email), null, authorities);
authentication.setDetails(
new WebAuthenticationDetailsSource().buildDetails(request));
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().setAuthentication(authentication);
}
}
} else {
log.debug(
"SecurityContextHolder not populated with security token, as it already contained: {}",
SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication()
);
}
chain.doFilter(request, response);
}
private Optional<String> getAccessToken(HttpServletRequest request) {
String token = request.getHeader(accessHeaderKey);
if (isNotBlank(token)) {
log.debug("Jwt token detected: {}");
try {
return Optional.of(URLDecoder.decode(token, "UTF-8"));
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error(e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
return Optional.empty();
}
private Optional<String> getRefreshToken(HttpServletRequest request) {
String token = request.getHeader(refreshHeaderKey);
if (isNotBlank(token)) {
log.debug("Jwt refreshtoken detected: {}");
try {
return Optional.of(URLDecoder.decode(token, "UTF-8"));
} catch (Exception e) {
log.error(e.getMessage(), e);
}
}
return Optional.empty();
}
private Jwt.Claims verify(String token) {
return jwt.verify(token);
}
private List<GrantedAuthority> getAuthorities(Jwt.Claims claims) {
String[] roles = claims.getRoles();
return roles == null || roles.length == 0
? Collections.emptyList() :
Arrays.stream(roles).map(SimpleGrantedAuthority::new).collect(
Collectors.toList());
}
}
- HTTP Request Header에 들어온 AccessToken을 이용해서 해당 AccessToken이 유효하다면 인증에 성공한다.
- 이제 다른 URL에 요청 시에도 AccessToken만 같이 보내준다면 인증되고 Authentication 정보를 조회해 올 수 있다.
GitHub - prgrms-web-devcourse/Team-03-LinkBook-BE: 강력3팀 북마크 공유 프로젝트(백엔드)
강력3팀 북마크 공유 프로젝트(백엔드). Contribute to prgrms-web-devcourse/Team-03-LinkBook-BE development by creating an account on GitHub.
github.com
자세한 코드 위 링크에서 보실 수 있습니다.
Reference
'프로젝트 > LinkBook' 카테고리의 다른 글
| RefreshToken 도입 (0) | 2022.08.23 |
|---|---|
| 토큰(JWT)기반 인증 도입 (0) | 2022.08.23 |
| 회원가입 이메일 인증 구현 (0) | 2022.08.21 |
| Batch Fetch Size를 통해 페이징 문제 해결 (0) | 2022.08.20 |
| 계층형 Category 구현 (Enum으로의 전환) (0) | 2022.08.19 |




댓글